Kawasaki ZR-7 and ZR-7S (1999-2005) Maintenance Schedule and Service Intervals
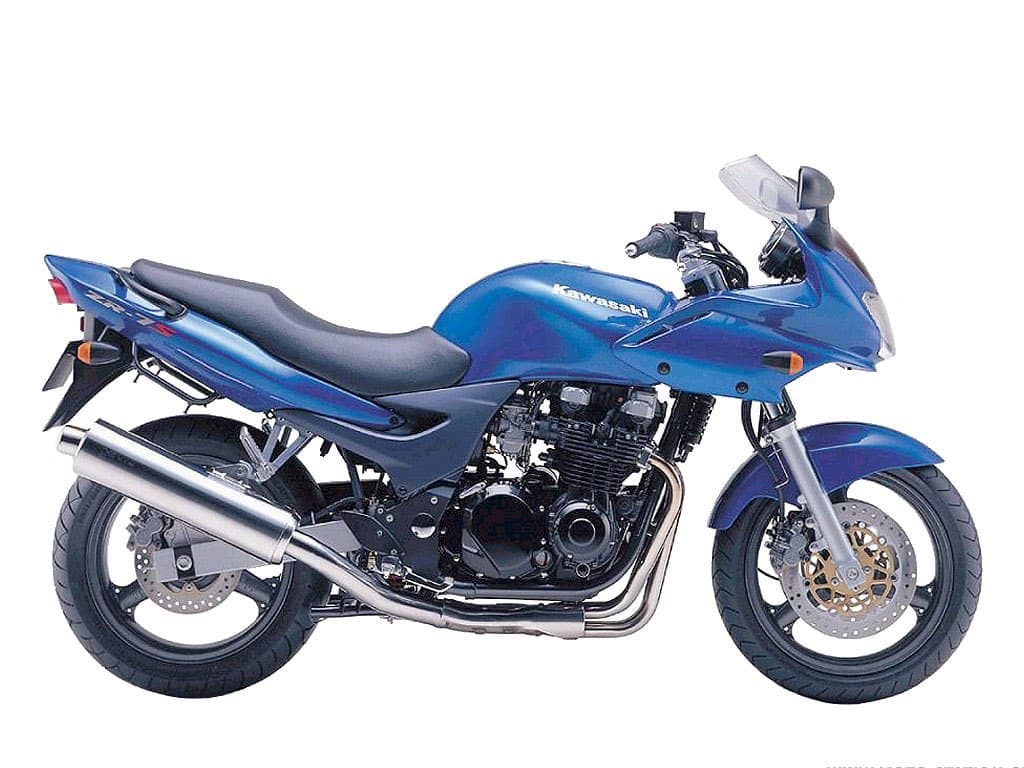
This is the maintenance schedule with associated service intervals for the Kawasaki ZR-7, also released in a fully faired version, the ZR-7S. The ZR-7 and the ZR-7S differ in fairing, headlight, instruments, and fork springs, but overall maintenance is the same.
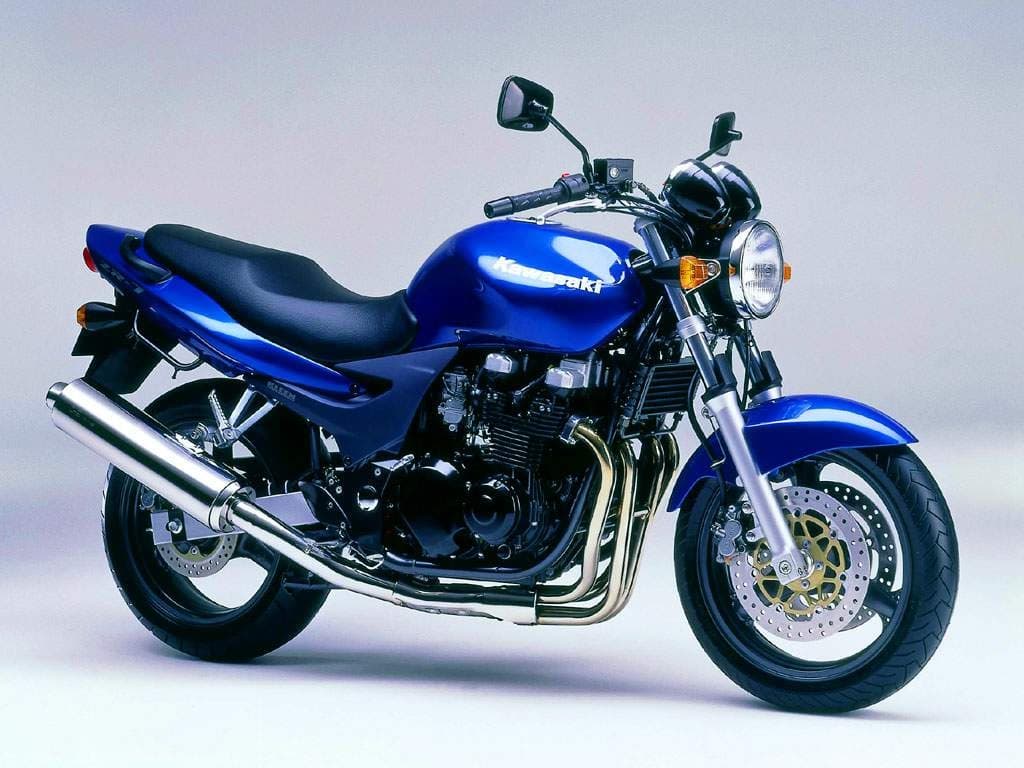
The Kawasaki ZR-7 / ZR-7S is based on a 738 cc air/oil-cooled inline four-cylinder engine. It’s fed by four 32 mm constant velocity carburettors and has a mild compression ratio of 9.5:1, which lets the engine develop peak power of 55.4 kW / 76 hp at 9500 rpm. Final drive is via a 5-speed gearbox and chain.
The Kawasaki ZR-7 was sold from 1999 to 2005, though sales were cut short in the US a little earlier. It was effectively replaced by the liquid-cooled Kawasaki Z750.
This site has links for things like oil and spark plugs from which we earn a commission (which unfortunately nobody can save, not even us). If you appreciate this work, then please use those links. Thanks!
Kawasaki ZR-7 / ZR-7S Service Intervals
The basic service interval for the Kawasaki ZR-7 or ZR-7S is every 3000 miles or 5000 km. At every service you have to check the plugs and sync the carbs, plus do a few safety-related checks.
You only need to change the oil on the Kawasaki ZR-7 every 6000 miles / 12000 km or every year. The valve clearance service interval is the same, but there’s no requirement to check the valves every year.
The Kawasaki ZR-7 has an air/oil-cooled engine so there’s no coolant to change. But you do have to keep the brake fluid fresh.
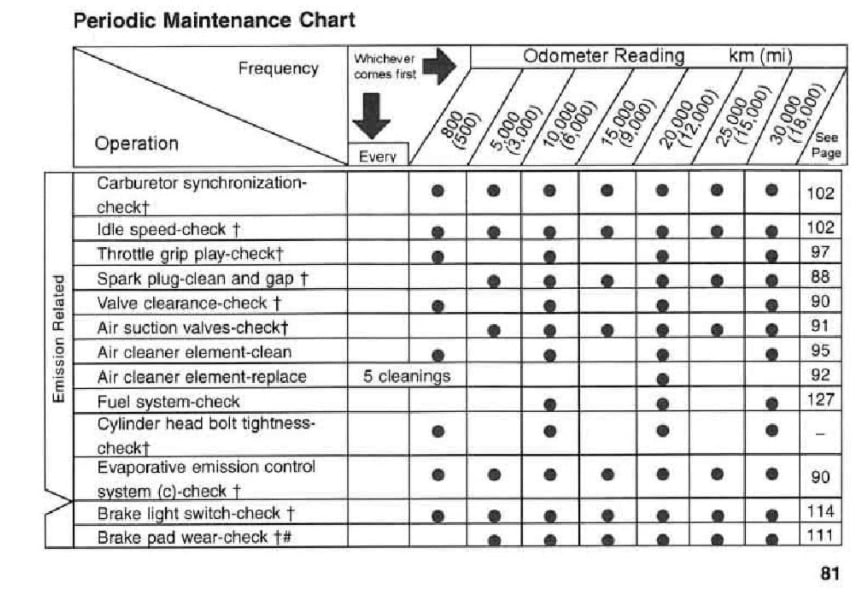
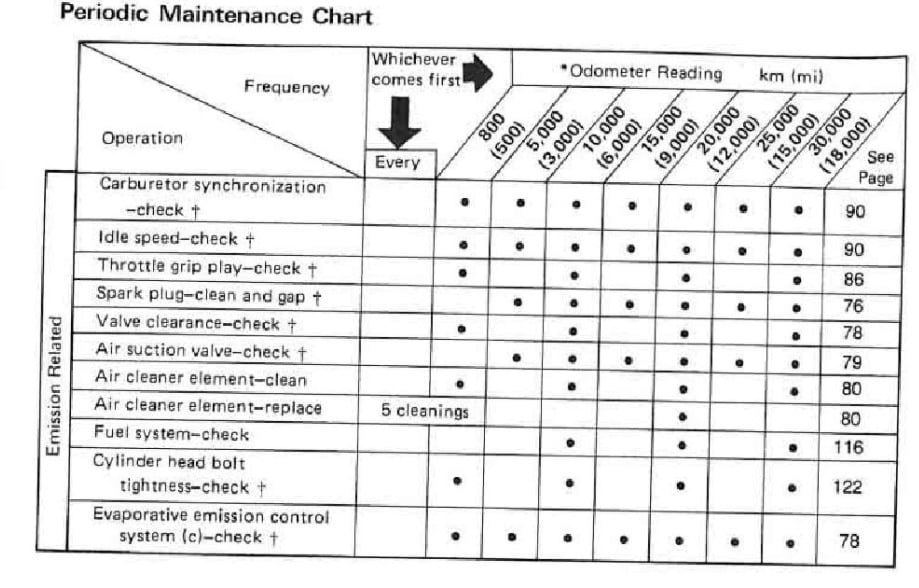
Maintenance Schedule for Kawasaki ZR-7 / S
Below is the maintenance schedule for the Kawasaki ZR-7 / S.
Notes:
- The following is the list of maintenance items be done on this motorcycle with a time or distance interval — whichever comes earlier.
- For higher odometer readings, repeat at the frequency interval established below.
- Kawasaki recommends you service safety or emissions-critical parts at a Kawasaki dealer.
- For items marked “check”, adjust, torque, or repair/replace as necessary.
- Service some items (chain, oil, filters) more regularly when riding in harsh conditions, e.g. dusty, dirt, rain, at high-speed or full throttle, or in low-speed traffic with lots of idling.
| mi x 1000 | 3 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 15 | 18 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| km x 1000 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | Every |
| Engine oil – change | • | • | • | year | |||
| Oil filter – replace | • | • | • | ||||
| Spark plug – clean and gap | • | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Carburetor synchronization – check | • | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Idle speed – check | • | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Air suction valves – check | • | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Valve clearance – check | • | • | • | ||||
| Throttle grip play – check | • | • | • | ||||
| Air cleaner element – clean | • | • | • | ||||
| Air cleaner element – replace | • | 5 cleanings | |||||
| Fuel system – check | • | • | • | ||||
| Cylinder head bolt tightness – check | • | • | • | ||||
| Evaporative emission control system (if fitted) – check | • | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Brake light switch – check | • | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Brake pad wear – check | • | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Brake fluid level – check | • | • | • | • | • | • | month |
| Brake fluid – change | • | 2 years | |||||
| Clutch – adjust | • | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Steering – check | • | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Drive chain wear – check | • | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Nuts, bolts, and fasteners tightness – check | • | • | • | ||||
| Muffler, exhaust pipe mounting nuts and bolts tightness – perform | • | • | • | ||||
| Tire wear – check | • | • | • | • | • | • | |
| General Lubrication – perform | • | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Swingarm pivot, uni-trak linkage – lubricate | • | • | • | ||||
| Front fork oil – change | • | ||||||
| Steering stem bearing – lubricate | • | 2 years | |||||
| Brake master cylinder cup and dust seal – replace | 2 years | ||||||
| Brake caliper piston seal and dust seal – replace | 2 years | ||||||
| Brake hose – replace | 4 years | ||||||
| Fuel hose – replace | 4 years |
Maintaining Your Chain on the Kawasaki ZR-7
The ZR-7 is a great everyday bike, so it’s doubly important to maintain the chain on it as it’s likely to be exposed to all kinds of elements. Use a good-quality chain lubricant like Motul chain paste, or a Motul chain care kit which comes with a couple of handy tools to maintain the chain.
Kawasaki recommends you follow the following chain maintenance schedule:
| Chain maintenance item | Every |
|---|---|
| Check drive chain lubrication condition, lubricating if necessary (Motul chain paste) | 400 mi / 600 km |
| Check drive chain slack, adjusting if necessary | 600 mi / 1000 km |
Notes:
- Do these items (checking/adjusting slack, and checking/applying lubrication) more often if you ride your ZR-7 in dusty or rainy conditions.
- Always lubricate the chain after washing the motorcycle.
Tyre size and tyre pressure for the Kawasaki ZR-7 and ZR-7S
The Kawasaki ZR-7 has the following tyres and tyre sizes standard (tubeless type), and the following recommended tyre pressures.
| Tyre | Size | Brand(s) | Tyre pressure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Front | 120/70 ZR17 (58W) | BRIDGESTONE BT020F RADIAL J DUNLOP D220 F ST MICHELIN MACADAM 100X | 250 kPa/36psi |
| Rear | 160/60 ZR17 (69W) | BRIDGESTONE BT020 R RADIAL DUNLOP D220 ST MICHELIN MACADAM 100X | 250 kPa/36psi |
About the Kawasaki ZR-7 and ZR-7S

The Kawasaki ZR-7 and its sibling the ZR-7S are a pair of simple everyday motorcycles, powered by an inline air/oil-cooled four-cylinder engine.
Kawasaki first brought the bike in in 1999, though you could easily mistake the ZR-7 for a bike that’s from the mid-seventies.
The engine is a very reliable one, with a low compression ratio of 9.5:1, and fed by four 32mm constant velocity carburettors. It has a double overhead cam design and four valves per cylinder.
The 738 cc engine is quite happy to rev, letting it make a peak of 55 kW / 76 hp at 9500 rpm, and peak torque of 63 Nm / 47 lbf-ft at 7500 rpm.
The final drive is via a five-speed transmission (with Kawasaki’s trademark positive neutral finder) and a chain. The positive neutral finder makes finding neutral easy when the bike is stopped.
The engine has a few tricks to make it very reliable. Even though it lacks liquid cooling, it has a high-capacity oil lubrication system, a 7-row oil cooler, and special jets that squirt cooler oil to the undersides of the high-compression pistons. All of this get the most out of the cooling capacity of oil.
The ZR-7 uses carburettors, but it also uses an electronic throttle position sensor for smooth throttle response. The Kawasaki’s ignition system reads the throttle position to adjusts the timing in response — even though fuelling is still by carburettor.
The suspension on the ZR-7 is quite basic, with a non-adjustable conventional fork, and a monoshock that’s adjustable only for preload. But the braking is capable, with twin 300 mm discs and two-piston calipers at the front.
The only strike against the Kawasaki ZR-7 is that at the time, it was outclassed by other bikes from other manufacturers, in particular the early Honda 599 / Honda Hornet, which with a liquid-cooled engine gave a far higher-power, sportier ride, and with lighter weight to boot (the ZR-7 is 210 kg dry, and the more powerful Hornet is just 183 kg dry).
Manual for the Kawasaki ZR-7 / S
The above maintenance schedule comes directly from the user’s manual for the 2001-2003 Kawasaki ZR-7S, which is available from Kawasaki directly.